In industrial production and environmental management, lime is an indispensable material. Whether in construction, metallurgy, chemical industries, or wastewater treatment and flue gas desulfurization, lime plays a crucial role. However, before lime can be used, it must undergo a critical process—Lime Slaking. Today, let’s delve into this seemingly simple yet scientifically intriguing process.


What is Lime Slaking?
Lime slaking refers to the process of reacting quicklime (CaO) with water (H₂O) to produce hydrated lime (Ca(OH)₂). This chemical reaction releases a significant amount of heat, which is why it is also known as "lime digestion" or "lime hydration."
The chemical equation is as follows:
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2+heat
Key Steps in Lime Slaking
- Raw Material Preparation
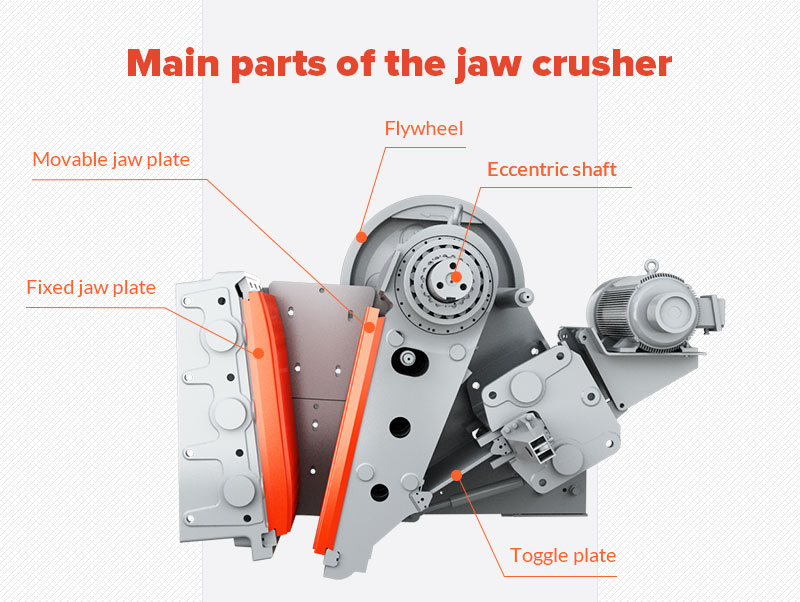
Quicklime (CaO) is typically produced by calcining limestone (CaCO₃) at high temperatures. Before slaking, the quicklime needs to be crushed into appropriate particle sizes to ensure thorough contact with water. - Water Addition and Reaction
Water is added to the quicklime, triggering a rapid reaction. This process releases a large amount of heat, raising the temperature to over 100°C, sometimes even causing the water to boil. - Mixing and Slaking
To ensure uniform reaction, the mixture is usually stirred. The resulting product is a fine lime slurry, which can be directly used in various industrial or environmental applications.
Applications of Lime Slaking
- Construction Industry
Hydrated lime is a traditional binding material used in mortar, plaster, and coatings. - Environmental Management
In wastewater treatment, hydrated lime is used to adjust pH levels and remove heavy metal ions. In flue gas desulfurization, it effectively absorbs sulfur dioxide (SO₂). - Chemical and Metallurgical Industries
Hydrated lime is a key raw material for producing calcium hydroxide, bleaching powder, and other chemical products. It is also used for desulfurization and dephosphorization in metal smelting. - Agriculture
Hydrated lime can improve acidic soils and provide essential calcium for plants.
Challenges and Optimization in Lime Slaking
Although lime slaking seems straightforward, it faces several challenges in practice:
- Heat Control: The release of substantial heat can damage equipment or pose operational risks, necessitating well-designed cooling systems.
- Reaction Efficiency: The particle size of quicklime, water addition rate, and mixing intensity all affect the slaking outcome.
- Product Quality: The concentration and fineness of the lime slurry directly impact its application performance.
To optimize the lime slaking process, modern industries often employ automated control systems to monitor temperature, pH, and mixing speed in real-time, ensuring efficient and safe operations.
Future Trends in Lime Slaking
With increasing environmental requirements and technological advancements, lime slaking technology is continuously evolving. For example:
- Green Processes: Developing low-energy, low-emission slaking equipment.
- Smart Control: Utilizing IoT and big data technologies for precise control of the slaking process.
- Multifunctional Applications: Exploring the potential of hydrated lime in new energy and material fields.
Conclusion
Lime slaking, this seemingly ordinary chemical reaction, embodies rich scientific principles and extensive application value. From construction sites to environmental projects, from farmlands to factories, hydrated lime is ubiquitous. It is this process of "turning the ordinary into the extraordinary" that makes lime a vital force in human societal development.